注册和登录
注册
使用独立的模块进行注册,控制器提供具体的路由,服务提供具体的注册服务
创建一个注册的模块:
nest g mo auth --no-spec针对数据库管理创建一个模块:
nest g mo prisma --no-spectsimport { Global, Module } from '@nestjs/common'; import { PrismaService } from './prisma.service'; @Global() // 将模块定义成全局的 @Module({ providers: [PrismaService], exports: [PrismaService], // 将服务暴露出去 }) export class PrismaModule {}在该模块中创建一个控制器:
nest g co auth --no-spectsimport { Body, Controller, Post } from '@nestjs/common'; import { AuthService } from './auth.service'; import RegisterDto from './dto/register.dto'; @Controller('auth') export class AuthController { // 将服务进行依赖注入 constructor(private readonly auth: AuthService) {} @Post('register') register(@Body() dto: RegisterDto) { return this.auth.register(dto); } }针对数据库管理,我们创建一个服务:
nest g s prisma --no-spectsimport { Injectable } from '@nestjs/common'; import { PrismaClient } from '@prisma/client'; @Injectable() export class PrismaService extends PrismaClient {}针对注册,创建一个服务:
nest g s auth --no-spec服务是来处理我们的具体业务的,服务之间可以有互相依赖(服务之间互相帮忙)
tsimport { Injectable } from '@nestjs/common'; import { PrismaService } from 'src/prisma/prisma.service'; import RegisterDto from './dto/register.dto'; import { hash } from 'argon2'; @Injectable() export class AuthService { // 注入PrismaService服务 constructor(private prisma: PrismaService) {} // 在服务中完善注册函数,提供给控制器使用,注册要提供注册的数据 async register(dto: RegisterDto) { // 对密码进行加密 const password = await hash(dto.password); // 使用查询构造器将内容提交到数据库 const user = await this.prisma.user.create({ data: { name: dto.name, password: password, email: dto.email, github: dto.github, avatar: dto.avatar, } }); return user; } }为了有类型支持,我们创建一个
dto文件,在src/login/dto/文件夹中创建register.dto.ts文件:tsimport { IsNotEmpty } from 'class-validator'; export default class RegisterDto { @IsNotEmpty({ message: '用户名不能为空' }) name: string; @IsNotEmpty({ message: '密码不能为空' }) password: string; email: string; github: string; avatar: string; }我们如果要使验证有效,需要绑定验证,我们要在入口文件
main.ts文件中,将验证管道进行全局绑定:tsimport { NestFactory } from '@nestjs/core'; import { AppModule } from './app.module'; import { ValidationPipe } from '@nestjs/common'; async function bootstrap() { const app = await NestFactory.create(AppModule); app.useGlobalPipes(new ValidationPipe()); await app.listen(process.env.PORT ?? 3000); } bootstrap();这样如果用户名或者密码为空的时候,就会显示其不能为空
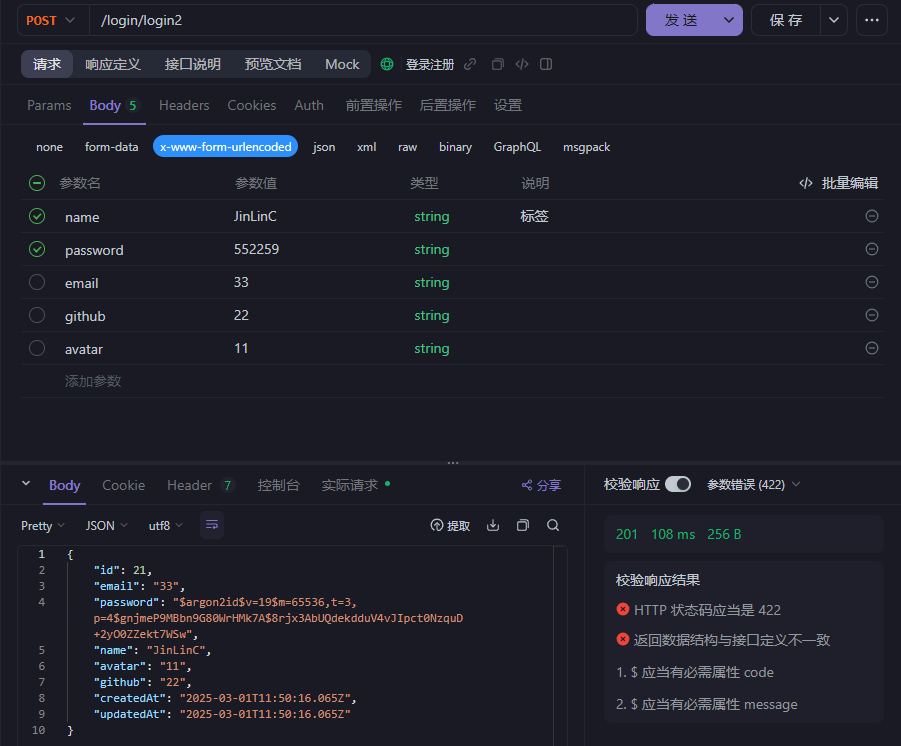
使用接口工具输入一个用户的信息:
显示发送成功,即实现了注册,同时我们可以在数据库的对应表中可以看到这条数据:
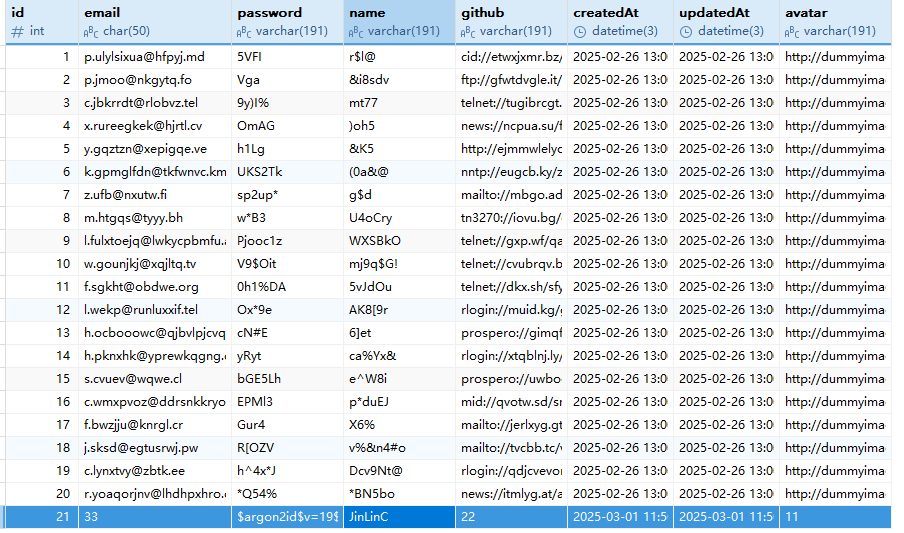
这样一个用户就注册成功了,同时密码也是加密的形式
登录
登录的逻辑在注册的逻辑上进行添加,登录的逻辑就是用户输入的用户名和密码都要在数据集中存在且正确
在注册控制器src/auth/auth.controller.ts文件中:
import { Body, Controller, Post } from '@nestjs/common';
import { AuthService } from './login.service';
import RegisterDto from './dto/register.dto';
import LoginDto from './dto/login.dto';
@Controller('auth')
export class AuthController {
// 将服务进行依赖注入
constructor(private readonly auth: AuthService) {}
// 注册
@Post('register')
register(@Body() dto: RegisterDto) {
return this.auth.register(dto);
}
// 登录
@Post('login')
login(@Body() dto: LoginDto) {
return this.auth.login(dto);
}
}对于登录的dto文件,在src/auth/dto/文件夹中创建login.dto.ts文件,由于和注册的dto文件比较相似,我们可以使用类型映射,从注册的dto文件中进行继承
import { PartialType } from "@nestjs/mapped-types";
import RegisterDto from "./register.dto";
// 继承注册的dto,将其类型都变成可选项
export default class LoginDto extends PartialType(RegisterDto){}就是将其复用过来,正常的验证不会受影响,如果有些数据不一样,对不一样的属性进行单独定义即可
在服务文件src/auth/auth.service.ts中完成登录的逻辑:
import { BadRequestException, Injectable, NotFoundException } from '@nestjs/common';
import { PrismaService } from 'src/prisma/prisma.service';
import RegisterDto from './dto/register.dto';
import { hash, verify } from 'argon2';
import LoginDto from './dto/login.dto';
@Injectable()
export class AuthService {
// 注入PrismaService服务
constructor(private prisma: PrismaService) {}
// 注册服务
// 在服务中完善注册函数,提供给控制器使用,注册要提供注册的数据
async register(dto: RegisterDto) {
// 对密码进行加密
const password = await hash(dto.password);
// 使用查询构造器将内容提交到数据库
const user = await this.prisma.user.create({
data: {
name: dto.name,
password: password,
email: dto.email,
github: dto.github,
avatar: dto.avatar,
}
});
return user;
}
// 登录服务
async login(dto: LoginDto) {
const user = await this.prisma.user.findFirst({
where: {
name: dto.name
}
});
// 如果用户不存在,抛出异常
if (!user) {
throw new NotFoundException('用户不存在');
}
// 检查 dto.password 是否存在
if (!dto.password) {
throw new BadRequestException('密码不能为空');
}
// 使用校对方法verify对密码进行校对
// 如果校对失败,提示密码输入错误
if (! await verify(user.password, dto.password)) {
throw new BadRequestException('密码输入错误');
}
return user;
}
}验证规则是用户在对应的数据表中必须存在,这样才能查询到完整的数据,否则就会抛出对应的异常: